Research Data Australia Functionality and Display
In addition to the information provided to the RDA Registry in RIF-CS format, Research Data Australia has the following display functionality built-in:
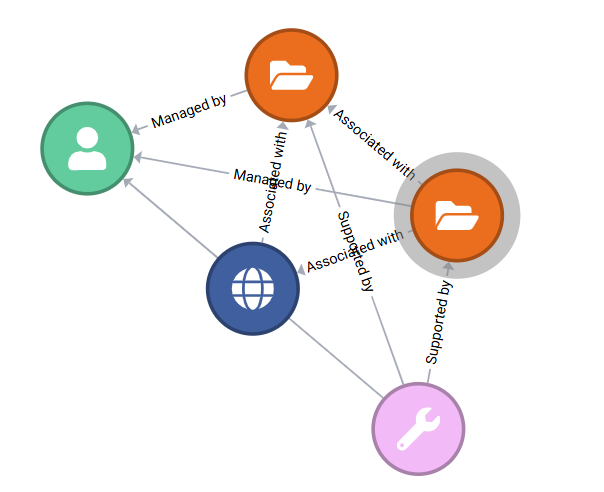
Relationships between registry objects
Primary relationships
Data Source Administrators can nominate two primary records that all other records within their data source are automatically linked to. This functionality makes it easier to manage a large number of links to a single object.
How it works: This capability is under the control of the contributor and is controlled by configuring the Data Source Account. The administrator can specify up to two primary record keys together with relations. The chosen primary records must be published and from the same data source. All records within the data source will then be linked to those primary (keystone) records and will display as related objects in Research Data Australia. This is an opt-in capability.
Bi-directional links between related objects
Research Data Australia can display links in both directions between related objects where the contributors have only provided one half of the relationship and have opted into this facility. This capability is under the control of the contributor and is controlled by configuring the Data Source Account. The default setting is to allow reverse links to be displayed for all related objects within a data source. However, a contributor can opt out of this setting. The inferred reverse links are created only for display purposes and cannot be edited. You can see them in Research Data Australia, and in the Registry view from Research Data Australia, but not in XML data.
A contributor can opt in to allow links to be shown from their records to records from a different data source, if that other data source has created a relation to one of the contributor's records. The default setting is not to allow reverse links to external data sources.
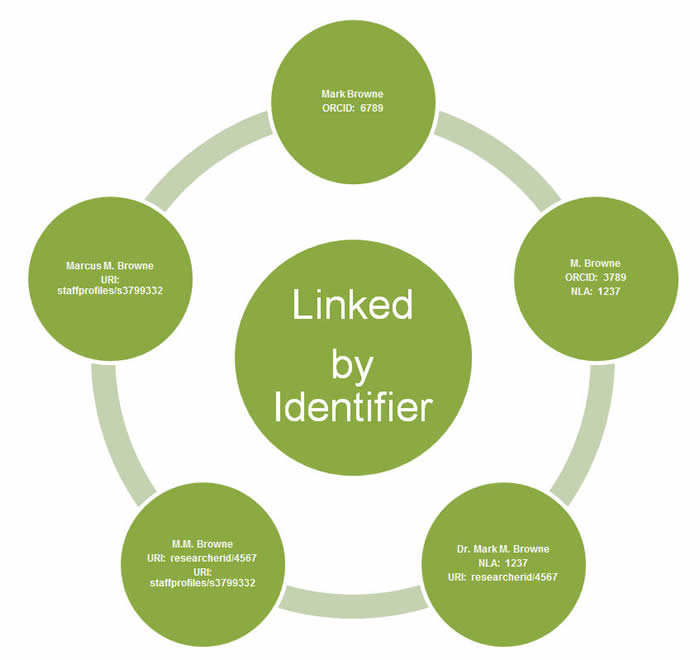
Registry objects linked by identifiers
Where two or more registry objects (from the same or different data sources) share a common identifier, the records will be treated as describing the same thing. In Research Data Australia, these records are merged into a single search result and links to each of the merged records are displayed on the view page of each record. Records from the same contributor are displayed as the primary result when merged.
On ingesting a record into the RDA Registry, the system will attempt to identify any other registry objects which share the same identifier. The match is made on both the full Identifier value (e.g. “1233-3453-3433-6643”) and Identifier Type (e.g. “orcid”).
Where one or more matches are discovered, the records are linked for display in Research Data Australia.
For party objects, if one or more of the matched records also contain a different identifier which has been linked to other party objects, these matched records will also be considered to be the same party and are linked as well. These five party records describe the same person and are linked by identifier.
Research graph display of relationships in Research Data Australia
Research Data Australia users see a visual presentation of a record's relationships through a relationship graph. Each node on the graph provides users with some basic information about the related entity and allows them to easily navigate to a linked page (e.g. ORCID page, RDA page, etc.), as applicable. If no related entity exists for that record, the graph is hidden from view.